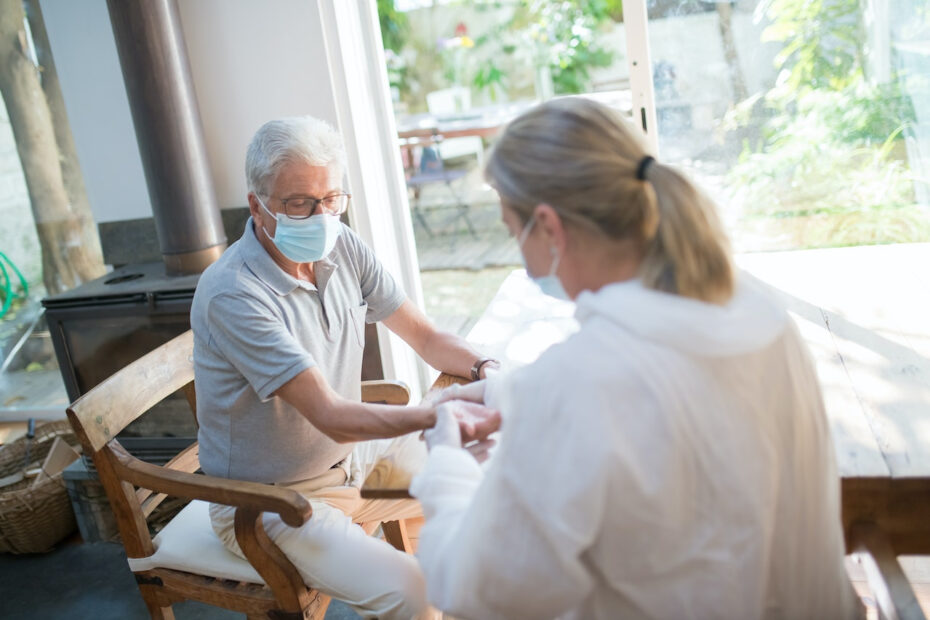
Occupational Therapy for Stroke Recovery & Regaining Independence and Quality of Life.
At La Gratitude, we believe that senior living should be about living life to the fullest, regardless of age or health condition. That’s why we offer a range of services to ensure that our residents receive the best possible care, including nutritional therapy, holistic care, and occupational therapy.
In our previous posts “Nutritional Therapy for Seniors – Improving Health and Well-being” and “Holistic Geriatric Care – Combining Traditional and Complementary Therapies”, we explored how these services can improve the quality of life for our residents.
In this blog post, we focus on the role of occupational therapy in stroke recovery. A stroke can be a life-changing event that affects a person’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being. But with the right care and support, stroke survivors can regain their independence and quality of life.
That’s where occupational therapy comes in.
Defining Stroke: Causes and Effects on the Body
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, either by a blockage in a blood vessel or by bleeding in the brain. As a result, the affected area of the brain is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, which can cause brain cells to die within minutes.
The impact of a stroke on the body depends on the severity and location of the stroke. Common symptoms include weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, and cognitive impairment.
Stroke survivors may also experience emotional and psychological changes, such as depression and anxiety. These effects can significantly affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities and lead to a loss of independence.
How Occupational Therapy Can Help Stroke Recovery
The role of occupational therapy in stroke recovery.
Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in stroke recovery by helping individuals regain their ability to perform daily activities and participate in meaningful occupations. Occupational therapists work with stroke survivors to assess their physical, cognitive, and emotional needs and develop personalized treatment plans to help them reach their goals.
Physical rehabilitation is a key aspect of occupational therapy in stroke recovery, which involves activities to improve mobility, strength, and coordination. Occupational therapists may also incorporate specialized techniques such as mirror therapy and constraint-induced movement therapy to help individuals regain their movement abilities.
In addition to physical rehabilitation, occupational therapists also address cognitive and emotional challenges that may arise after a stroke. This can involve strategies to improve memory and attention, as well as techniques to manage emotions and improve mood.
Occupational therapy focuses on adapting the patient’s environment and using assistive devices to facilitate daily activities. This can include modifying the home environment, prescribing assistive devices such as walkers or wheelchairs, and providing training on how to use these devices effectively.
The key aspects of stroke recovery.
Occupational therapy is a key aspect of stroke rehabilitation and plays a crucial role in helping patients regain their independence and improve their quality of life. Here are some ways occupational therapy can help:
- Improving physical function: Occupational therapists work with stroke survivors to improve their physical function, including a range of motion, strength, and coordination. This may involve exercises and activities to help the patient regain control over their movements and reduce any physical limitations.
- Addressing cognitive deficits: After a stroke, some patients may experience cognitive deficits such as memory loss, difficulty with problem-solving, or impaired attention. Occupational therapists can help by providing cognitive rehabilitation, which can involve exercises and activities that improve memory and cognitive function.
- Managing emotional challenges: Stroke survivors may experience emotional challenges such as depression or anxiety, which can impact their quality of life. Occupational therapists can provide support and guidance to help manage these emotions, improve mood, and promote overall well-being.
- Adapting the environment: Occupational therapists can help stroke survivors modify their environment to make daily activities easier and safer to perform. This may include adding handrails or grab bars, rearranging furniture, or using assistive devices such as walkers or wheelchairs.
- Providing education and training: Occupational therapists can provide education and training to both the patient and their family members to help them understand the recovery process and how to support the patient. They can also provide training on how to use assistive devices effectively to improve independence.
By addressing these aspects of stroke recovery, occupational therapy helps patients regain their independence, improve their quality of life, and achieve their goals. The ultimate goal of occupational therapy is to help patients return to the activities that they find meaningful and important, whether that’s going to work, spending time with family, or pursuing hobbies and interests.
Examples of interventions used by occupational therapists.
Here are some examples of interventions that occupational therapists often use in stroke recovery:
- Range of motion exercises: Occupational therapists can use exercises to help stroke patients regain mobility and improve their range of motion.
- Activities of daily living (ADL) training: Occupational therapists can teach stroke patients how to perform ADLs, such as dressing, grooming, and feeding, using adaptive equipment or modifying the task to fit their abilities.
- Cognitive and perceptual retraining: Occupational therapists can help stroke patients improve their cognitive and perceptual abilities by using techniques such as memory and problem-solving exercises.
- Sensory re-education: Occupational therapists can help stroke patients who have lost sensation in their limbs or other parts of their body regain their sense of touch and improve their proprioception.
- Energy conservation techniques: Occupational therapists can teach patients how to conserve energy and manage their fatigue levels by prioritizing tasks, pacing themselves, and taking breaks.
- Environmental modifications: Occupational therapists can modify the patient’s environment to improve safety and accessibility, such as adding grab bars in the bathroom, removing clutter, and installing ramps.
- Leisure and social participation: Occupational therapists can help stroke patients re-engage in leisure activities they once enjoyed, and provide opportunities to connect with others and participate in social activities.
The Benefits Of Occupational Therapy For Stroke Patients
Let’s take a closer look at the specific benefits of occupational therapy for stroke patients.
Occupational therapy aims to help stroke patients regain their ability to perform daily activities, such as dressing, grooming, and eating. Through a combination of exercises and specialized equipment, occupational therapists can help patients regain their functional abilities and improve their quality of life.
Stroke patients are at a higher risk of falls due to balance and mobility issues. Occupational therapists can work with patients to develop strategies to improve their balance and reduce the risk of falls. These strategies may include exercises to improve balance and coordination, as well as the use of mobility aids, such as canes or walkers.
Occupational therapy can help stroke patients regain their independence by developing strategies to manage daily activities on their own. This may include teaching patients how to use adaptive equipment or modifying their living environment to accommodate their needs.
Stroke patients may experience cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulty with attention and problem-solving. Occupational therapists can develop cognitive rehabilitation plans to help patients improve their cognitive function and manage daily tasks more effectively.
In cases where stroke patients experience depression, anxiety, or other mental health issues due to the impact of stroke on their lives. Occupational therapy can provide a supportive environment for patients to discuss their feelings and develop coping strategies to manage their emotions.
Examples regarding communication and mobility issues.
Communication
Stroke patients may experience difficulties with speech and language, so occupational therapists can work with them to improve their communication skills. This may include exercises to strengthen the muscles used in speech, training in using alternative communication methods such as writing or gestures or working with speech-language pathologists to develop a personalized communication plan.
Mobility
Occupational therapists can help patients regain their ability to move around and perform physical activities safely and independently. This may involve exercises to improve balance, strength, and coordination, as well as training in using assistive devices such as walkers or canes. In some cases, occupational therapists may work with physical therapists to develop a comprehensive mobility plan for the patient.

The Occupational Therapy Process
Occupational therapy is a patient-centred approach to rehabilitation that aims to help individuals recover and regain independence in their daily lives. The process typically begins with an assessment to determine the patient’s needs and areas of concern.
Assessment
During the assessment, the occupational therapist will evaluate the patient’s functional abilities, including their physical, cognitive, and emotional abilities. They may also consider the patient’s home environment, social support system, and personal goals.
Goal Setting
After the assessment, the occupational therapist will work with the patient to set goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The goals will be tailored to the patient’s needs and preferences and may include tasks related to activities of daily living (ADLs), mobility, communication, and community reintegration.
Treatment Planning
Once goals are established, the occupational therapist will develop a treatment plan that outlines the interventions and activities that will be used to achieve those goals. The treatment plan may include a combination of physical exercises, cognitive interventions, and emotional support.
Interventions
Occupational therapy interventions for stroke patients may include the following:
- ADL training.
- Mobility training.
- Cognitive training.
- Emotional support.
- Community reintegration.
- Environmental modifications.
The different stages of stroke recovery.
After a stroke, patients often experience different stages of recovery, each with its own challenges and needs. The stages of recovery are typically broken down into acute, sub-acute, and chronic phases.
Occupational therapy can be beneficial throughout each of these phases, but the focus and goals of treatment may vary.
In the acute phase, which occurs immediately after the stroke, the patient is typically in a hospital setting and may still be undergoing medical interventions. The occupational therapist may focus on maintaining a joint range of motion, preventing contractures, and addressing any immediate safety concerns, such as positioning and transferring in bed. The therapist may also provide education to the patient and family members about the stroke, potential impairments, and strategies for managing any deficits.
During the sub-acute phase, which typically lasts for several weeks to months after the stroke, the patient may be in a rehabilitation centre or at home. Occupational therapy during this phase focuses on helping the patient regain function and independence in activities of daily living, such as dressing, grooming, bathing, and toileting.
Sometimes, the therapist works on improving cognitive and communication skills and mobility, such as transfers, walking, and using assistive devices.
During the chronic phase, which can last for years after the stroke, the patient may be living at home and may have ongoing deficits. Occupational therapy during this phase focuses on adapting the patient’s environment and tasks to maximize independence and safety.
This may involve modifications to the home, such as installing grab bars, ramps, and stair lifts, and using adaptive equipment, such as reachers and dressing aids. In some cases, the therapist may also work on community reintegration and participation in meaningful activities, such as hobbies and social events.

Choosing an Occupational Therapist for Stroke Recovery
Here are some tips on how to choose an occupational therapist for stroke recovery:
- Look for a licensed and certified occupational therapist who has experience in stroke recovery.
- Check if the therapist has experience working with patients with similar conditions and recovery goals to yours.
- Consider the location and accessibility of the therapist’s office, especially if you have mobility issues.
- Check the therapist’s availability and flexibility to accommodate your schedule and recovery needs.
- Look for a therapist who can communicate effectively and build a good rapport with you.
- Ask for referrals or recommendations from your primary care physician or other healthcare professionals.
- Consider the cost and insurance coverage for the therapist’s services.
- Finally, trust your instincts and choose a therapist who makes you feel comfortable and confident in your recovery journey.
The Importance Of Finding A Therapist Who Specializes In Stroke Recovery
Finding an occupational therapist who specializes in stroke recovery and has experience working with stroke patients is crucial for a successful recovery process. Stroke recovery is a complex and unique process that requires specialized knowledge and skills.
A therapist who has experience working with stroke patients can assess the individual’s needs, abilities, and limitations and develop a personalized treatment plan to promote recovery.
The right therapist will have a deep understanding of the effects of stroke on the body and the specific challenges that stroke patients face in their daily lives. They will have experience working with patients at different stages of recovery and can adjust their treatment plans accordingly.
An appropriate therapist will have a network of healthcare professionals that they can collaborate with to provide the patient with comprehensive care. This includes working with a physical therapist, speech therapist, and other healthcare providers to ensure the patient receives the best care possible.
In addition to specialized knowledge and skills, a therapist who specializes in stroke recovery may have access to specialized equipment and technology that can aid in the recovery process. For example, they may have access to equipment designed to improve mobility or communication skills.

Consider Occupational Therapy For Stroke Recovery
In this post, we learned that occupational therapy plays a vital role in the recovery process for stroke patients. The objectives are to help individuals regain their independence and improve their quality of life by addressing physical, mental, and emotional challenges.
Through specific interventions, occupational therapists assist stroke patients with daily activities, communication, and mobility. The process of occupational therapy involves assessment, goal setting, and treatment planning, and may vary depending on the stage of stroke recovery.
When seeking an occupational therapist, it is important to find someone who specializes in stroke recovery and has experience working with stroke patients.
At La Gratitude, we understand the importance of Occupational Therapy in stroke recovery. Therefore, we have the ability to integrate occupational therapy tailored to each of our residents who may require it, due to our close proximity to the hospital.
Thank you for your continued support, we appreciate your likes, follows and retweets on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest and LinkedIn. Make sure to share this post with friends and family.
You can make a difference
With your assistance, the volunteers at La Gratitude will be able to take better care of not only the residents at the old age home but also the greater Newcastle community. La Gratitude is constantly involved in outreach projects to help the elderly in need in and around Newcastle.
Your donations will be greatly beneficial in the provision of food and other basic necessities for the less fortunate elderly people that require assistance.
Donating is easy, click here to donate now.




